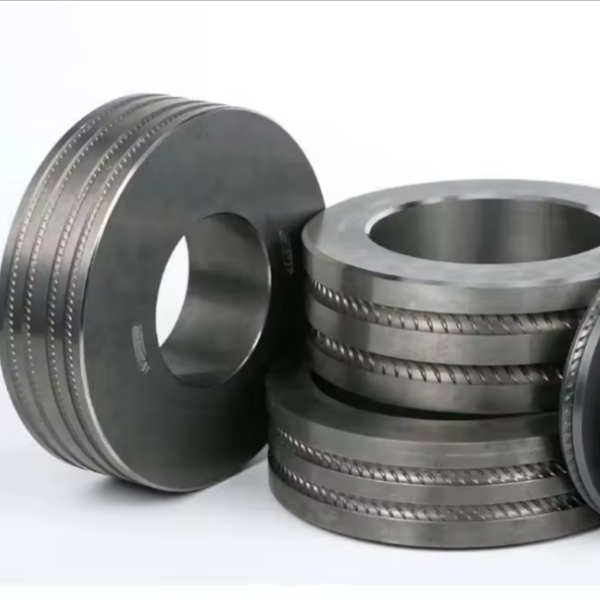
Tungsten carbide hot rolling rolls are widely used in various industrial applications, especially in the manufacturing and processing of metal products. These rollers are known for their durability, high temperature resistance and excellent wear resistance. However, despite the many advantages of tungsten carbide heat rollers, there are also some disadvantages associated with their use. In this blog, we’ll take a closer look at the disadvantages of using tungsten carbide heat rollers and explore potential challenges and limitations that users may encounter.
One of the main disadvantages of tungsten carbide hot rolling rolls is their high cost. Tungsten carbide is a premium material known for its exceptional hardness and heat resistance, but this comes at a price. The manufacturing process of tungsten carbide hot rolls involves complex processes and the use of expensive raw materials, resulting in higher production costs compared to rolls made of other materials. Therefore, the initial investment required to purchase tungsten carbide hot rolls can be much higher, making them difficult for some businesses (especially small businesses with limited budgets) to obtain them.
Another disadvantage of tungsten carbide hot rolling rolls is their brittleness. While tungsten carbide is known for its hardness, it is also inherently brittle, which can make the roll susceptible to cracking or chipping, especially under high stress conditions. This brittleness can be a serious problem in industrial applications where the rolls are subjected to heavy loads, rapid temperature changes or abrasives. The risk of damage due to brittleness may require frequent maintenance and replacement of rollers, resulting in increased downtime and maintenance costs for the user.
Additionally, tungsten carbide heat rollers are known for their high thermal conductivity, which is both an advantage and disadvantage. While tungsten carbide’s excellent heat resistance enables rolls to withstand extreme temperatures without deformation, high thermal conductivity also results in rapid heat transfer during the rolling process. This can lead to uneven temperature distribution on the roll surface, which can lead to thermal stress and deformation. In some cases, rapid heat transfer can also affect the material being processed, causing problems such as surface defects or inconsistent product quality.
In addition to being brittle and thermally conductive, tungsten carbide heat rollers are susceptible to corrosion in certain environments. While tungsten carbide itself is highly resistant to corrosion, the bonding materials used to make the rolls, such as cobalt or nickel, can be susceptible to chemical attack in certain industrial environments. Exposure to corrosive substances or harsh operating conditions can cause roll surface degradation, compromising its performance and life. Therefore, users of tungsten carbide thermal rollers need to carefully evaluate the roller’s compatibility with their specific operating environment to mitigate the risk of corrosion-related problems.
Finally, machining and regrinding tungsten carbide hot rollers can present challenges due to the material’s extreme hardness. Tungsten carbide ranks very high on the Mohs scale of mineral hardness, making it particularly difficult to machine or grind. This limits the feasibility of repairing or refurbishing worn or damaged rolls, as the process of reshaping or reconditioning rolls requires specialized equipment and expertise. The difficulty of machining tungsten carbide hot rolls can result in higher maintenance costs and longer roll repair intervals, affecting the overall operating efficiency of equipment using these rolls.
In conclusion, while tungsten carbide heat rollers offer excellent performance and durability in high-temperature industrial applications, they are not without their drawbacks. High cost, brittleness, thermal conductivity, susceptibility to corrosion and processing challenges are important factors to consider when evaluating the suitability of tungsten carbide hot rolled rolls for a specific manufacturing process. Despite these shortcomings, advances in materials science and manufacturing technology continue to drive improvements in the performance and reliability of tungsten carbide heat rollers, addressing some of the limitations associated with their use. By understanding potential challenges and limitations, users can make informed decisions and implement appropriate measures to maximize the benefits of tungsten carbide hot rolls while mitigating their drawbacks.
Mia wang E-mail: hengrui@hrcarbide.cn
Post time: Jul-20-2024