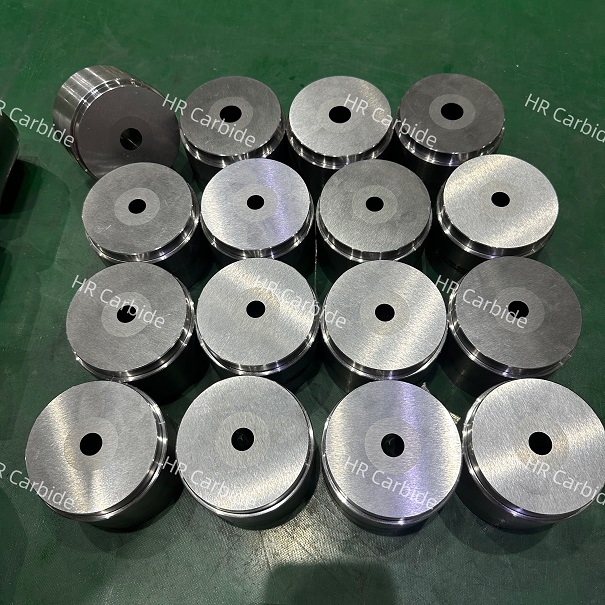
Tungsten carbide and high-speed steel, identify grinding wheel sparks. The deep red sparks are high-speed steel. If you hit it with a hammer without a grinding wheel, the alloy will be easily brittle. You can also test it with a magnet. Carbide does not absorb, but high-speed steel can. .
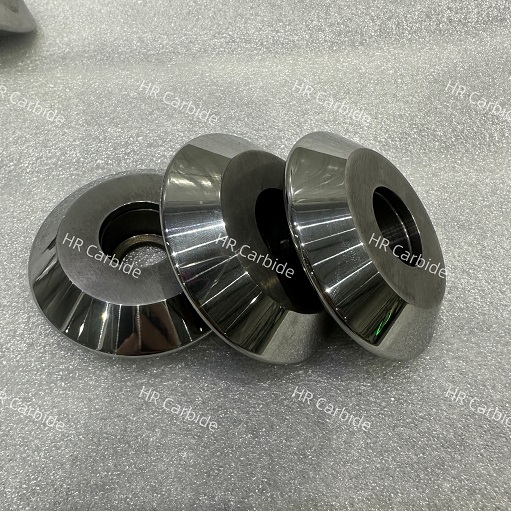

Tungsten carbide cemented carbide is an alloy material made from hard compounds of refractory metals and bonding metals through a powder metallurgy process. Cemented carbide has a series of excellent properties such as high hardness, wear resistance, good strength and toughness, heat resistance, and corrosion resistance. In particular, its high hardness and wear resistance remain basically unchanged even at a temperature of 500°C. , still has high hardness at 1000°C. Carbide is widely used as tool materials, such as turning tools, milling cutters, planers, drill bits, boring tools, etc., for cutting cast iron, non-ferrous metals, plastics, chemical fibers, graphite, glass, stone and ordinary steel, and can also be used for cutting Heat-resistant steel, stainless steel, high manganese steel, tool steel and other difficult-to-process materials.
High-speed steel is a tool steel with high hardness, high wear resistance and high heat resistance. It is also called high-speed tool steel or front steel, commonly known as white steel. High-speed steel was created by F.W. Taylor and M. White in the United States in 1898. High-speed steel has good process performance and a good combination of strength and toughness. Therefore, it is mainly used to manufacture complex thin blades and impact-resistant metal cutting tools. It can also be used to manufacture high-temperature bearings and cold extrusion dies. In addition to high-speed steel produced by smelting methods, powder metallurgy high-speed steel appeared after the 1960s. Its advantage is that it avoids the reduction of mechanical properties and heat treatment deformation caused by carbide segregation caused by smelting production.
Post time: May-09-2024